
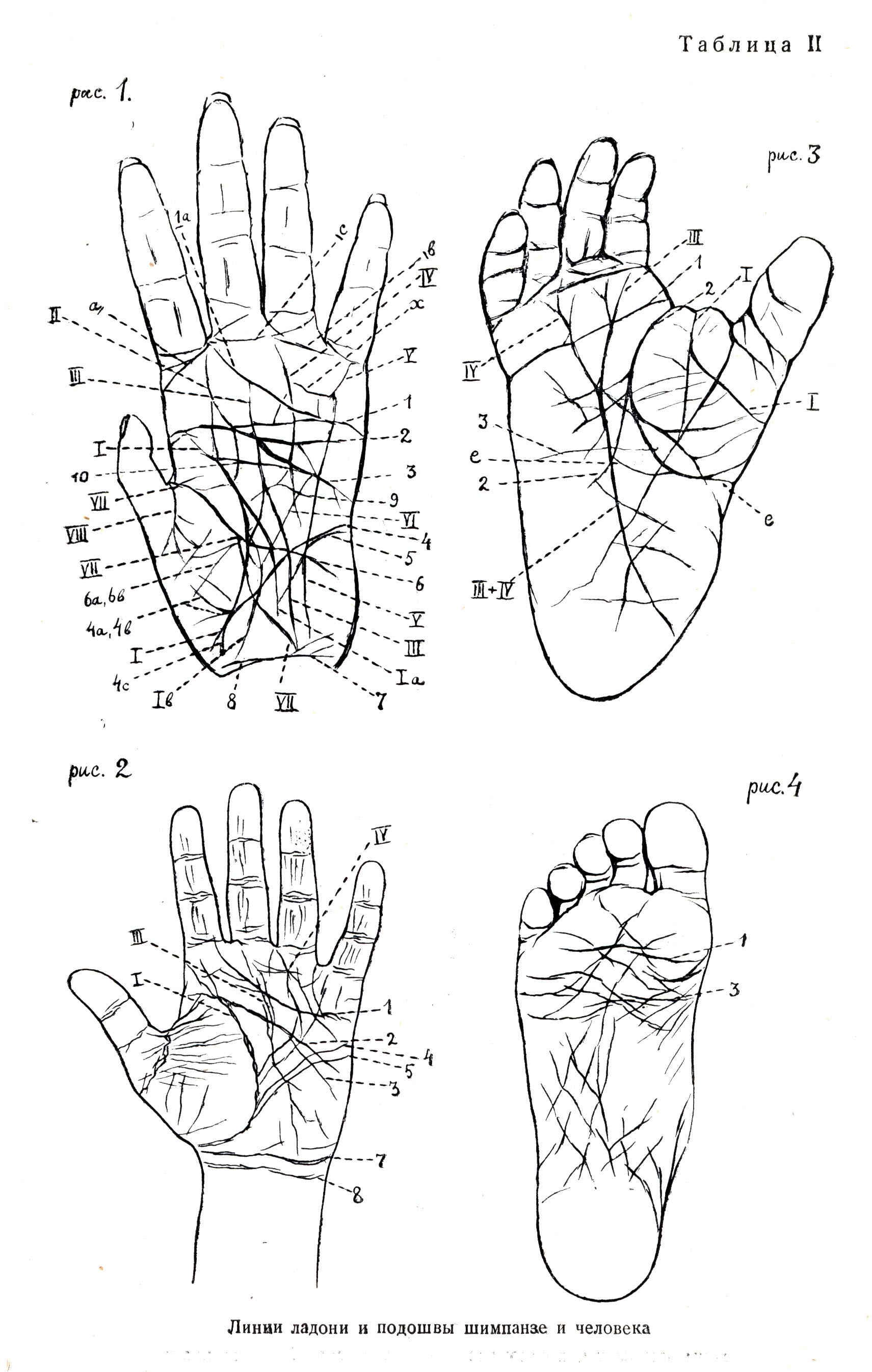
The incisors are large and broad, the canines are sexually dimorphic and occlude in such a way as to maintain their sharp tips, while the premolars and molars are relatively small. incisors and canines) than posterior teeth (i.e. The extant species of Pan, like other extant apes, are distinguished by their pronounced supraorbital tori and long projecting lower faces that house relatively larger anterior teeth (i.e. The facial skeletons of Homo sapiens and its closest living relatives in the genus Pan differ considerably. The major evolutionary trends in the hominin lineage subsequent to the LCA are discussed in relation to the dental arcade and dentition, subnasal morphology and the size, position and prognathism of the facial skeleton.
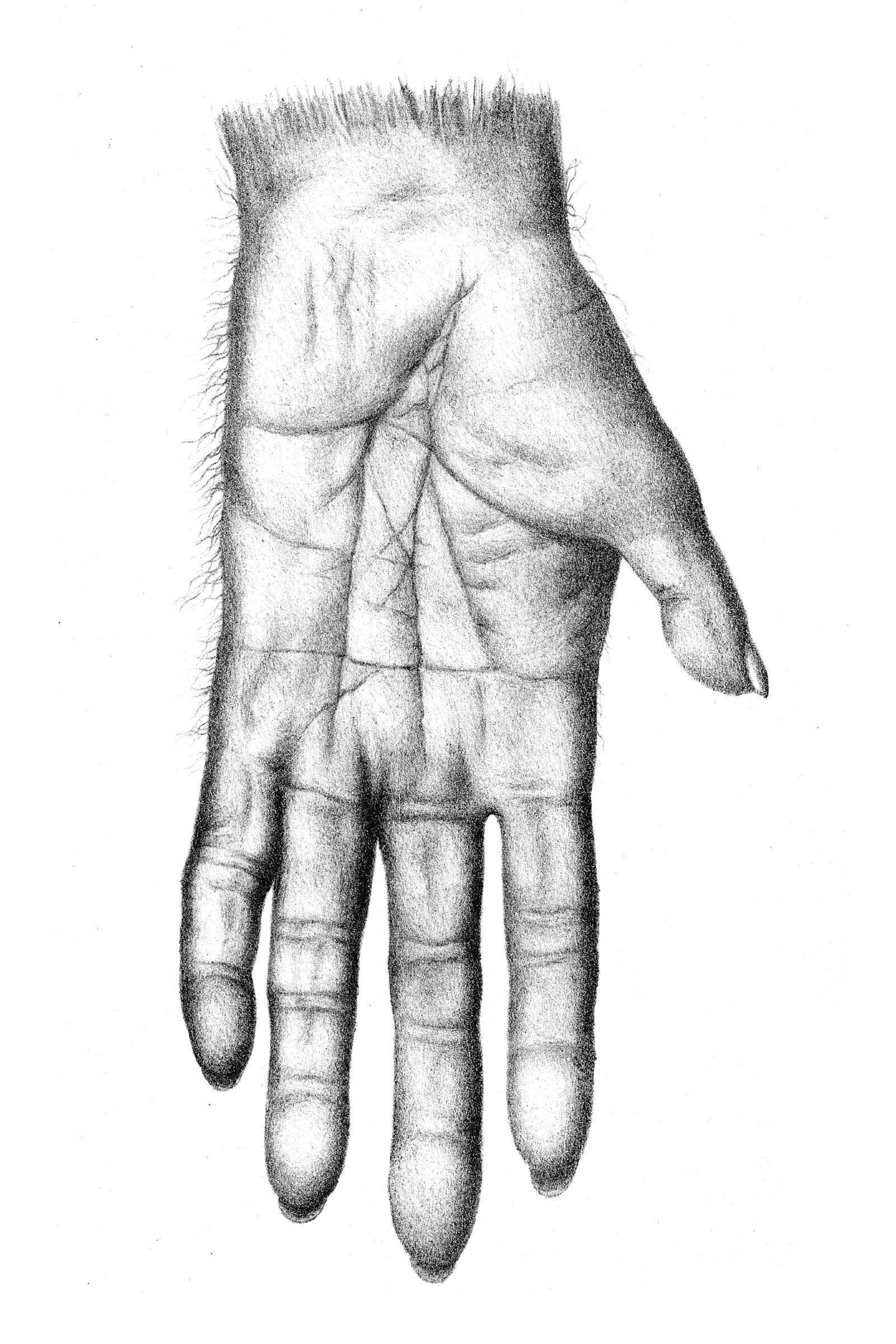
It is not possible to determine with any confidence whether the facial morphology of any of the current candidate LCA taxa ( Ardipithecus kadabba, Ardipithecus ramidus, Orrorin tugenensis and Sahelanthropus tchadensis) is representative of the LCA, or a stem hominin, or a stem panin or, in some cases, a hominid predating the emergence of the hominin lineage.
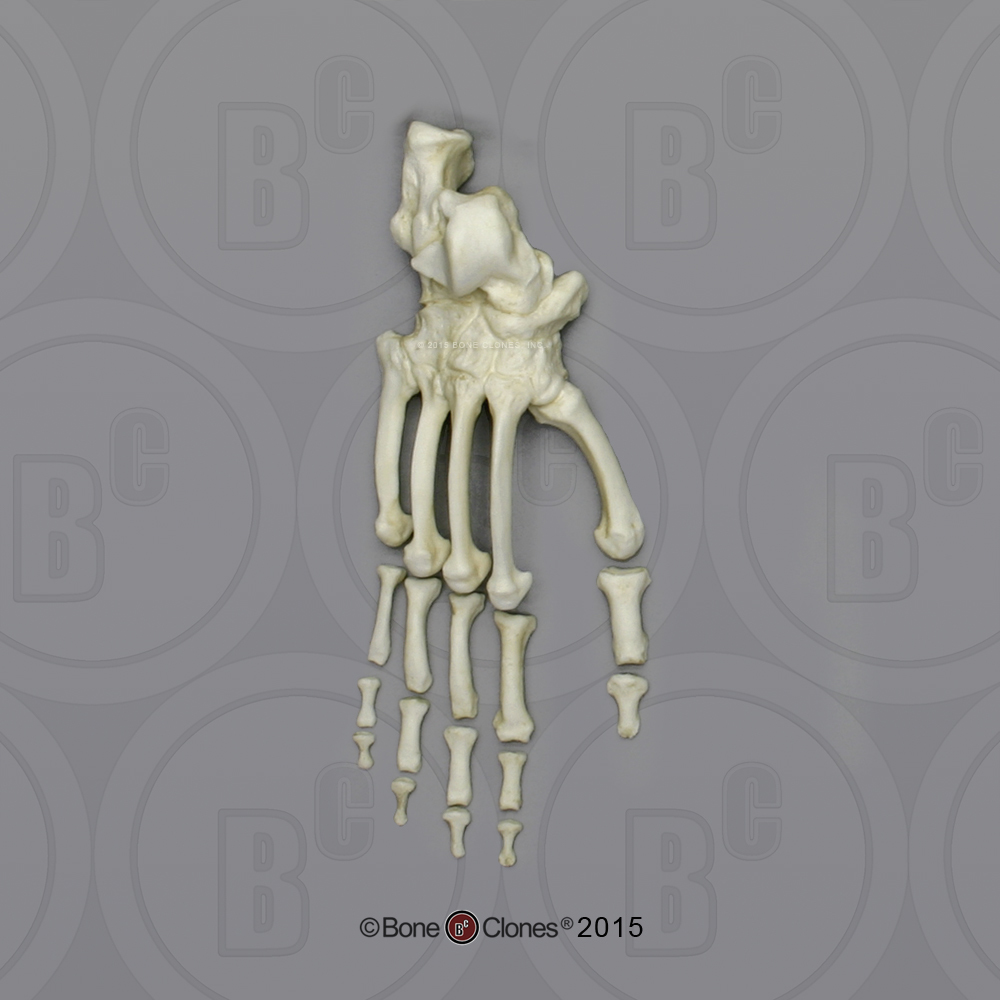
Consequently the list of hypothetical features expected in the face of the LCA is very limited beyond its hypothesized similarity to extant Pan. These include the prevalence of homoplasy and poor phylogenetic resolution due to a lack of defining derived features. Some of the problems involved in reconstructing ancestral morphologies so close to the formation of a lineage are discussed. This review uses the current morphological evidence to evaluate the facial morphology of the hypothetical last common ancestor (LCA) of the chimpanzee/bonobo (panin) and human (hominin) lineages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
